When reading our blog posts, you might find yourself asking what the scale of the black holes, jets, or accretion disks we speak of are. If that is the case, then this post is for you! Given that Halloween just happened, let us choose our base unit as one Jack-o’-lantern pumpkin (JOLP) that is 20 kg heavy and 0.5 meters in diameter. For scale, roughly four JOLPs stacked on top of each other would span a human that is 1.8 meters tall and 80 kg heavy. Right, then how many JOLPs would we need to span the entire circumference of the Earth? Well, we would need about 80 million (80…
Read More >>The Science Behind the Solar Eclipse (Part II)
This is the second and final part on the series of blogposts titled “The Science Behind the Solar Eclipse”. In this post, I will build upon the ideas and concepts discussed in Part I of the post to describe how solar eclipses occur. So I strongly recommend reading through it here. Solar eclipses occur because of the Moon blocks the Sun, as viewed from some point on Earth. As elucidated in Part I, due to the varying distance between the Earth and the Moon, the Moon may block the Sun in its entirety or a portion of it. Another way to think about this is the geometry of the Earth,…
Read More >>Electron Microphysics in the global GRMHD simulation
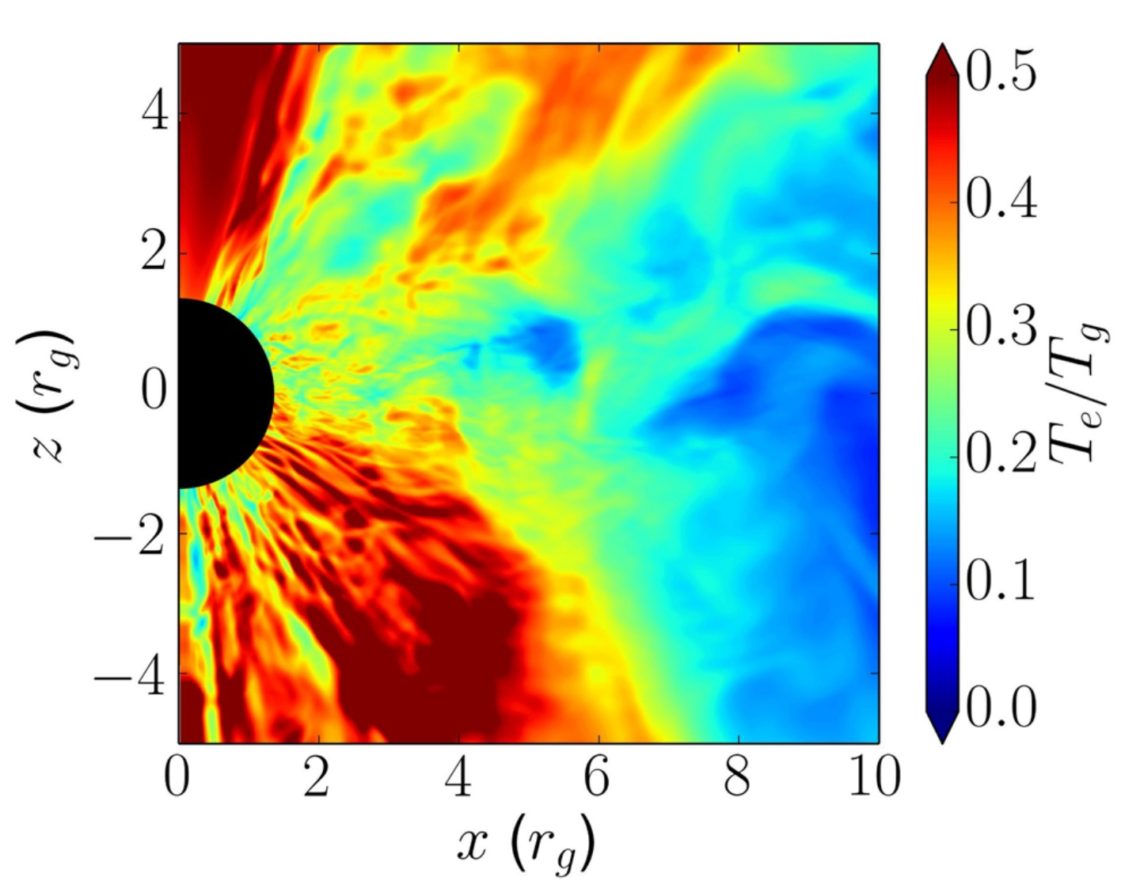
It is widely believed that the luminosities of M87 and Sagittarius A*, which are the major targets of the Event Horizon Telescope collaboration, are significantly lower than their Eddington luminosities. It means that the mass accretion rates of these objects are so low that the material accreting onto the central supermassive black hole can be interpreted as the radiatively inefficient accretion flow (RIAF), which is geometrically thick and optically thin (See “disk thin / thick?!” for the disk models). In such a (geometrically) thick disk, it is generally acceptable to assume that the interactions between ions and electrons are very poor, so they are not in thermal equilibrium, resulting in…
Read More >>When you’re a JET…
No, not the West Side Story musical kind… (although they are awesome) The Jets gang from West Side Story. So our research group is called Jetset. We work on trying to figure out the physical processes that launch jets of matter and light from (very close to) black holes. So what are these jets actually? In the astrophysical sense, jets are linear beams of charged particles like protons and electrons (aka plasma) that are emitted along the rotation axis of an astrophysical object, like a black hole. Jets launched from black holes reach speeds close to the speed of light. These super fast moving outflows of plasma exhibit the effects…
Read More >>Black Holes, the most Powerful Engines in Nature
Energy source is an eternal topic of human development, as any activity in nature requires a supply of energy. In ancient times, nearly all production work relied on human or animal power, resulting in very low productivity for thousands of years. The Industrial Revolution in the 18th century changed this situation completely, replacing human labour by machines powered by burning fuels. Combustion of chemical fuels is the most widely adopted energy source in the current world, for both domestic and industrial purposes. In such a process, the chemical energy of the fuels are first transformed into thermal energy, which is then used to power various machines to do work. How…
Read More >>New World, New Life
Hi there! My name is León Sosapanta and will arrive at the University of Amsterdam in September this year to join Sera Markoff’s group as a Ph.D. student. My research will focus on theoretical modeling of black hole accretion, particularly using numerical/computational techniques in the code H-AMR, to better understand the physics implemented within these simulations of black holes, starting by including new processes that allow the separate treatment of hadrons and leptons, and the effects of hadron acceleration. This work will allow the same models used to interpret Event Horizon Telescope sources to also be compared with multi-wavelength and multi-messenger data including very-high-energy gamma-rays and neutrinos. All my college…
Read More >>You know you are a theorist when…
You know you are a theorist when you find yourself solving problems that were “left as an exercise for the reader”. You might even know you are a theorist when your default hypothesis for a weird astrophysical phenomenon isn’t just “because of magnetism”. I have not been able to relate to these statements until this year — better late than never! Originally a student whose work was based on observational astronomy, I was introduced to theoretical astrophysics in 2019 when I visited the Jetset group to work on a winter project. I worked with Dr Thomas Russell and Prof. Sera Markoff in collaboration with other members of the group to…
Read More >>From BIG to small, accretion built them all
Our research group is composed almost entirely of theorists. They create models and simulations, based on physics, to try to figure out how black holes work. I’m an observational astronomer, I gather data from telescopes and try to figure out how black holes (and neutron stars) work. The thing that we’re all trying to figure out is this process called accretion. In other words, the process by which black holes pull matter from their surroundings or a companion star into themselves via gravity. This process increases the black hole mass, powers its rotation and is linked to the launching of jets of matter and light from around black holes. In…
Read More >>A sky full of… PeVatrons
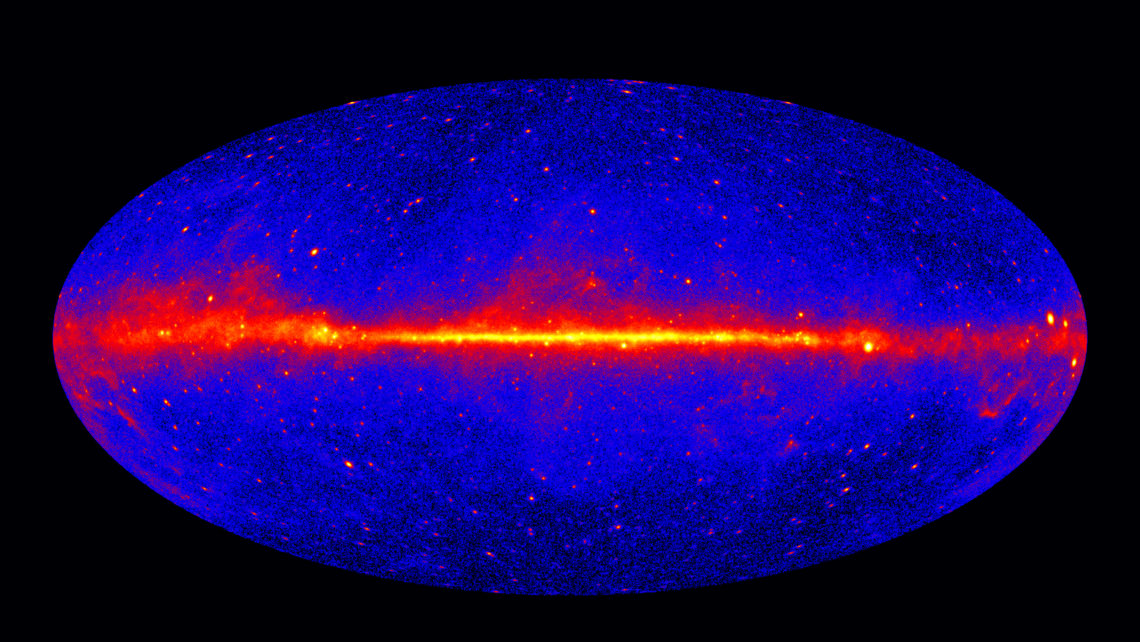
‘Cause you’re a sky, ’cause you’re a sky full of starsI’m gonna give you my heart‘Cause you’re a sky, ’cause you’re a sky full of stars‘Cause you light up the pathI don’t care, go on and tear me apartI don’t care if you do, ooh ooooh oooooooh ooooooooohhhh Uhh sorry, I really like this song! I think if Coldplay were to sing this song today, they would write: ‘Cause you’re a sky, ’cause you’re a sky full of Pevatrons… oohh oooooooh (great tune, isn’t it?) But what are PeVatrons that would make Coldplay change their hit? Let’s travel to the distant East, somewhere in the Tibetian plateau (unless you read…
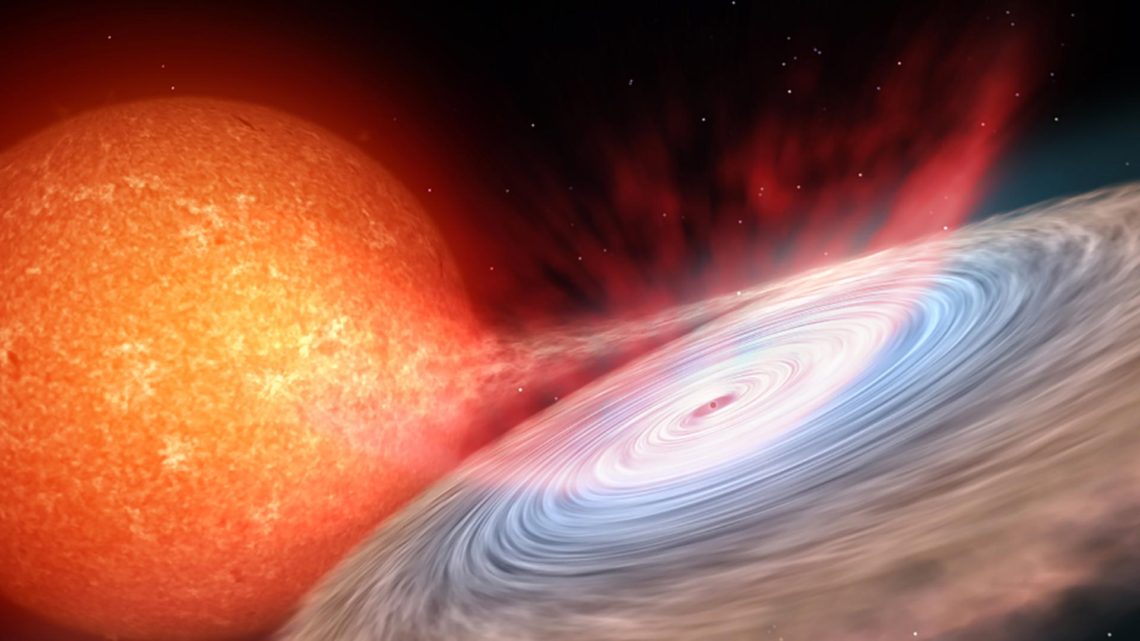
Read More >>Black hole accretion and quasi-periodic oscillations
Quasi-periodic oscillations appear to be a common characteristic of accreting systems and have been observed in black hole and neutron star X-ray binaries, alongside active galactic nuclei and even ultraluminous X-ray sources. The focus of this blog post is quasi-periodic oscillations in black hole X-ray binaries. Black hole X-ray binaries are comprised of a stellar mass black hole feeding on a nearby star. Material siphoned off the star by the black hole swirls around the black hole, forming an accretion disk that shines brightly at X-ray frequencies (see Figure 1). Not all of the material in the disk is consumed by the black hole- hydro-magnetic processes in the inner regions…
Read More >>